| |
English Synonyms Page
By Leon
This page is particularly helpful to ESL/EFL
Students of the English language!!!
BUT, it is ALSO useful for
young native-speaker students who wish to increase their vocabulary!!!
|
Foreword
One of the best ways to improve your "word power" is
to know the special meanings, nuances and differences in USAGES
of English synonyms.
Firstly, you need to know what "hypernomy" or
"hypernymy" means...
hyper (above) + nomy (name)
Hypernomy is the condition of being
inclusive of all other synonymy of a given set of synonyms.
Hypernym is the word which includes the meanings of all
the other synonyms.
Like this:
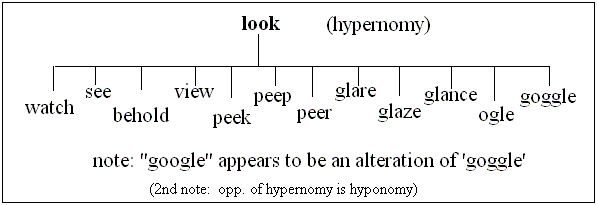
In the diagram above, the word "look" is a
hypernym, and the diagram illustrates the hypernomic condition of
"look".
|
Table of Contents
(The contents are not in any specific
order, except the order that they came to my mind.)
| 1. speak, talk, say, tell, mention, discuss, converse, comment |
| 2. argue, debate |
| 3. hear, listen, comprehend |
| 4. boat, ship, sail boat, yacht, motor boat, ferry, row boat, canoe,
kayak, raft |
| 5. look, watch, see, stare, behold, view, peek,
peep, peer, glare, glaze, glance, ogle, goggle |
| 6. school, academy, institute, college, university |
| 7. walk, saunter, strut, stroll,
hobble, limp, stumble, stagger, ambulate, shuffle |
| 8. ghost, phantom, spirit, soul,
apparition, specter, sprite, banshee, disembodied spirit, un-embodied
spirit, devil, Devil, demon, Satan, Lucifer, angel, Holy Ghost, ghoul, goblin,
zombie |
| 9. effective & efficient |
| 10. job, profession, vocation, occupation |
| 11. holiday, vacation |
| 12. electric, electrical, electronic |
| 13. excrement, feces, stool, crap, shit, defecation, manure |
| 14. accept,
receive, take |
| 15. include,
contain, have |
| 16. be
made of, be made from, be composed of, consist of |
| 17. land,
territory, earth, ground, soil, dirt |
| 18. beach,
shore, coast, ~side, bank |
| 19. wide,
broad, vast, huge |
| 20. had better / have to &
must / ought to & should |
| 21. home, house, housing,
abode, domicile, dwelling, dormitory, barracks |
| 22. attire, apparel, clothes,
clothing, garment, vestiture, wear |
| 23. kinds of attire |
| 24. faculty and staff |
| 25. folktale, folklore, legend, myth |
| - END - |
| You will need
to scroll down for contents. I apologize for the inconvenience. |
Abbreviations Used Below:
v. = verb
v.t. = verb transitive (needs an object)
v.i. = verb intransitive (doesn't use an object)
|
Speak, Talk, Say, Tell, Mention, Discuss, Converse,
Comment |
|
|
| Speak
(v.i., v.t.)
|
Speak has two usages [Speak comes from the noun speech
which also has two usages]:
1. Speech1 = the ability to produce the
SOUNDS of words and sentences accurately; This is related to
"Speak" v.i. AND "Speak"
v.t., where the
direct object is a language.
Examples: (i) He speaks well. (ii) He
speaks poorly.
(iii) He has a
speech impediment. (iv) He speaks English well.
(v) I speak Chinese poorly.
2. Speech2 = an oral composition, presented
in front of an audience; This is related to "Speak"
v.t.
where the direct object is an audience (it looks like an indirect
object, but it's not, usually).
Examples: (i) Pres. Bush spoke to the troops
in Korea. (ii) Pres. Bush gave a speech to the troops in Korea.
Note: it is possible to use a direct object and an indirect
object, but it is not common.
Examples: (i) I spoke English to my
students. [but in this case "spoke" has the number 1
meaning only].
If you say, "I spoke in English to my
students" "spoke" has the number
two meaning, and there is only one object, because "in
English" is an adverbial phrase.
|
| Talk (v.i., v.t.) |
Talk means 'have a conversation'. It's that
simple.
Examples: (i) I talk. (ii) I talk with
you. (iii) We talk about the price of tea in China.
|
| Say (v.t.) |
Say is a confusing word. In all my life growing up
in the states, moving around from California to West Virginia, I had
NEVER heard ANY native English speaker put the indirect object before
the direct object (with the ONE exception of reflexive pronoun object)
and I taught my students in Korea thusly. Then, about a year ago,
I went to the UK for a couple months, and I heard a UK citizen
(apparently a native English speaker) use the indirect object
first. I was so embarrassed. Now, I teach my students that
in the UK it is not uncommon to hear the indirect object first, but if
one goes to America and uses the indirect object first, the Americans
will hear it as an awkward expression of a non-native speaker.
direct object:
something (sth)
indirect object: (to)
somebody (sb)
American style: say + sth
+ to + sb
Example: I said "I
love you" to my son.
in the UK, I would seem that the direct object and indirect object are
interchangeable, but the indirect object must have "to" before
it.
|
| Tell (v.t.) |
In the case of "tell", the direct object and
indirect object are the opposite of "say".
direct object: sb
indirect object:
(about) sth
Example: I told him
about the party.
Note: the indirect object is optional, AND IT IS INCORRECT TO
SWITCH THE ORDER OF DIRECT AND INDIRECT OBJECT.
There are a few idiomatic expressions which break the rule I gave
above:
For example: (i) Tell a story. (ii) Tell a joke.
In those cases, the direct object has been omitted, when it is
commonly known "who" the direct object is.
Example of full sentence: Tell us
a story.
|
| Mention (v.t.) |
Mention means to reveal some information briefly. |
| Discuss (v.t.) |
Discuss means to have a conversation on a specific topic |
| Converse |
Same as "talk" |
| Comment |
Usually comment on sth already
said |
|
Argue & Debate |
| |
| Argue |
Argue means to have a verbal fight
v.i. : Don't argue with me.
v.t. : Why argue about politics? Nobody wins.
|
| Debate |
Debate means to have a formal verbal competition with
rules and a judge, and a winner and a loser. [forgive my many "and"s].
v.i. : I like to debate.
v.t. : Let's debate about politics.
|
|
Hear, Listen, Comprehend |
|
|
| Hear |
Hear denotes ability to perceive sound; in other
words, it means having a fully-functional auditory nervous system. |
| Listen |
Listen denotes hearing + trying to comprehend what is
being said |
| Comprehend |
Comprehend denotes understanding input;
Listen and Comprehend, or Read and Comprehend |
|
Boats
ship, sail boat, yacht, motor boat, ferry, row boat, canoe,
kayak, raft |
| |
| boat |
general term for all items below |
| ship |
an very large commercial boat or military boat |
| sail boat |
a boat with a cloth/canvas for a sail |
| yacht |
a recreational sail boat or motor boat |
| motor boat |
a relatively small privately owned boat with a motor
engine |
| ferry |
a boat for transporting people or vehicles from point A to
point B and back |
| row boat |
a small boat with oars for rowing |
| canoe |
a small, long, two-person boat (American Aborigine word) |
| kayak |
a small, one-person boat (Eskimo word) |
| raft |
a small boat, generally for life-saving or rescue |
|
Look
Watch, See, Stare, Behold, View, Peek, Peep, Peer, Glare, Glaze,
Glance, Ogle, Goggle, |
| |
| look |
general usage, hypernomy or hypernymy of all words below; requires the preposition "at" before
the object |
| watch |
look at something
that
moves
We say, "Watch TV" because the picture portrayed by the TV
moves. If you want to see the TV, and NOT the picture portrayed by
the TV, use "look at".
We say, "Watch a person" because people move.
It would be incorrect to say, "Watch a plant", unless it is
a moving plant. You could say, "Watch(ed) the leaves on the trees
as they 'dance(d)' in the wind" because the leaves are moving. |
| see |
"see" generally denotes visual perception,
i.e., the ability to take input in the form of
LIGHT
into the brain via the optic nerve.
Example: "I can see the dog. Can't you?"
It Can be used as a command. Example:
"See the dog run." But this usage is archaic.
BUT, there are several idioms with the word "SEE"...
1. I see.
"I see" means "I understand", or "I am
enlightened by your words". NOTE: light = knowledge or
understanding, and since light is perceived through the eyes, "I
see" has the meaning: I receive light (or
ENLIGHTENMENT). Also, the expression "to see the light"
means: to apprehend truth
2. see a movie
You could also say, "watch a movie". I do not know
how "see a movie" came to be acceptable speech, but it
is. |
| behold |
"behold" means "look", but no
preposition is needed.
Example: I beheld the duck in the pond.
NOTE: this word is archaic |
| view |
look
somewhat formal usage
Example: "The immigration officer viewed my
passport."
Also: preview [pre (before) + view (look)] and,
review [re (again) + view (look)] |
| peek |
look very briefly at something forbidden to be
looked at
Example: "I peeked at my Christmas present." |
| peep |
secretly look (+ at sth)
"Peeping Tom" is a man, who secretly looks at a woman
undressing from outside her bedroom window |
| peer |
look (+ through sth) |
| glare |
angrily look (+ at sth) |
| glaze |
casually look (+ over sth) |
| glance |
briefly look (+ at sth) |
| ogle |
lustfully look (+ at sth) |
| goggle |
surprisedly look (+ at sth) |
|
School, Academy, Institute, College,
University |
| |
| school |
place of learning; [hypernomy
of all words below (in U.S. ONLY)]
If you want to be specific, you should add an adjective:
1. public/private elementary school
2. public/private middle school or junior high school
3. public/private high school
4. state/private school of higher learning (college or university) |
| academy |
usually private school AND often one that teaches 1 subject, e.g., the academy of art. |
| institute |
1. a school of higher learning
Example: MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
2. a place of extra-curricular learning
Example: Smithsonian Institute |
| college |
"college" is a very general word from Latin collegium
"community, society, guild."
If you want to be specific, you should add an adjective:
1. junior college "J.C."
2. community college (same as 1)
3. college of art (in a university)
4. college of science (in a university)
A "colleague" is usually a person who is in the same
academic field AND/OR in the same profession. |
| university |
similar to institute1; BUT, a university usually contains
various colleges, e.g.:
1. the university's college of education
2. the university's college of life science
3. the university's college of physical science
4. the university's college of art
5. the university's college of mathematics
6. the university's college of humanities
7. the university's college of engineering
8. the university's college of behavioral science
etc.
Note: it is not difficult to comprehend the differences between
"college" an "university" if you know the etymology
of each word.
"College" means a groups of people interested in the same
thing(s) "Uni" (one) + "versity" (many) = one
school with many colleges. |
etymology: the study of the origin of words
|
walk, saunter, strut, stroll,
hobble, limp, stumble, stagger, ambulate, shuffle |
| |
| walk |
to move on foot (hypernomy or hypernymy of all below) |
| saunter |
to walk idly, leisurely |
| strut |
to walk proudly |
| stroll |
same as saunter |
| hobble |
to walk as if one leg is lame |
| limp |
same as hobble |
| stumble |
to trip |
| stagger |
to walk as if drunken or weak |
| ambulate |
to go from place to place on foot |
| shuffle |
to walk without picking up one's feet |
|
ghost, phantom, spirit, soul,
apparition, specter, sprite, banshee, disembodied spirit, un-embodied
spirit, devil, Devil, demon, Satan, Lucifer, angel, Holy Ghost, ghoul, goblin,
zombie |
| |
| ghost |
[Old English Word] a metaphysical being (hypernomy or
hypernym of all
below) |
| phantom |
[Latinate Word] a ghost that can be seen, but not touched;
OR heard, but not seen (but usually the latter, i.e., heard, but NOT
SEEN) |
| spirit |
[Latinate Word] the breath of life |
| soul |
[Old Norse Word] same as spirit; the immortal part of
humans |
| apparition |
[Latinate Word] something that suddenly appears (usually a
ghost) |
| specter |
[Latinate Word] a visible disembodied spirit {same root as
"spectacle", "spectator"} |
| sprite |
[originally, same as spirit] BUT now it means: elf or fairy
(incidentally, this would be much like the Korean do-ggae-bi, not in
physical traits, but rather in all other traits. Physically, the
do-ggae-bi looks like an ogre, and is translated as such, but do-ggae-bis
do not harm humans, in fact, they're often thought of as the benefactors
of human beings.) |
| banshee |
[Gaelic Word] a female spirit in Gaelic folklore that
warns a family of the approaching death of a member by her appearance or
especially by wailing unseen under the windows of the house a night or
two before the time of the death she foretells (Merriam-Webster online
Dictionary) {This is most similar to Korean 처녀귀신 (Cheo-nyeo Gui-shin}.
|
| disembodied spirit |
the spirit of a dead person |
| unembodied spirit |
the spirit of an unborn person |
| devil |
[Old English Word] an evil spirit |
| Devil |
king of the evil spirits |
| demon |
[Greek Word] originally: a lower deity (between gods and
humans); now: a devil that can become incarnate, or take a
human body. |
| Satan |
[Hebrew Word] name of king of the devils |
| Lucifer |
[Latinate Word] means: one who bears light or
enlightenment.
It is the Latinate metaphor for Satan, because Satan was a "son of
the morning", one of the first of the creations of God. (Judaeo-Christian
mythology). Lucifer is also the one who gave enlightenment to Adam
and Eve. |
| angel |
[Greek Word] originally: messenger; now: messenger
of God |
| Holy Ghost |
the Spirit of God (Judaeo-Christian mythology) |
| ghoul |
[Arabic Word] a being that robs graves to feed on the
flesh of dead people |
| goblin |
an ugly sprite, sometimes evil, sometimes mischievous |
| zombie |
[Voodoo Word] (1) the power to make the dead alive again;
(2) a
dead person that has been brought back to life |
|
Effective & Efficient |
| |
| Note: these are NOT synonyms, but the
English-Korean dictionaries say that they have the same meaning.
This is to dispel such nonsense. |
| Effective |
producing the desired effect (result) [from the
root word "effect" v.t.: to produce or cause sth]
Example: I wanted to build a bridge.
I built a bridge in ten years. I was effective.
Why? Because I accomplished my goal, which was to build a bridge. |
| Efficient
bilingual dict error
|
conserving something [from the root word
"efface" v.t.: to eliminate or eradicate sth]
Example: I wanted to build a bridge.
I built a bridge by myself in ten years. It was effective.
Then, I built a bridge in two years with the help of some workers. It was time-efficient. But, I had to pay them a lot
of money. It was NOT cost-efficient. Also, I used wood,
which is not as strong as stone or steel, so I had to use a lot of wood
to reinforce the bridge. It was NOT material-efficient.
Then, I built a bridge with migrant workers in two years with steel
and concrete. It was effective, time efficient, cost-efficient,
and material-efficient.
Another Example: I want to buy a car that is effective in
giving me speed and power AND efficient in conserving fuel and money.
I find out that I cannot have both. I can get an effective car,
but it is not efficient. Or I can get an efficient car, but it's
not very effective. |
|
job, profession, vocation, occupation |
| |
| job |
...any activity which is compensated with money
full time job = job which works 40 hours per week or more [US]
part time job = job which works less than 40 hours per week
[US] |
| profession |
...any job which requires higher education, esp., doctor,
lawyer, nurse, teacher, engineer, scientist, etc. |
| vocation |
"Voc" means "voice" in Latin.
"Vocare" means "to voice" (v.t.). So,
"vocation" means something that is done because the
"voice" in one's mind directs one to do it. It usually
refers to a job that one feels driven to do by some inner
"voice". |
| occupation |
...any activity which occupies one's time. "To
occupy" means "to fill". So, an occupation is
something which fills one's spare time. (It usually refers to the
thing which fills the major part of one's time). |
| holiday, vacation |
| |
| holiday |
1. holy day [like Christmas, Easter,
Halloween]
2. a day (or days) off of work/school [chiefly British]
3. a festival day (sometimes it is a day off, and sometimes
it's not) [chiefly American English] |
| vacation |
1. a day (or days) off of work/school
2. a trip |
| examples |
sb be/go on holiday (#2, British English)
sb be on vacation. (#1, American English)
sb go on vacation. (#2, American English)
Today is a holiday. (#2, British, #3, American) |
|
electric, electrical, electronic |
| |
| electric (a.) |
of, about, relating to electricity
examples: electric shock, electric power, electric resistance,
electric current, electric flow, etc. |
| electrical (a.) |
conveying electricity
examples: electrical wires, electrical components, etc. |
| electronic (a.) |
having a system which is operated by electrical
wires and components
examples: electronic equipment, electronic device, etc. |
| special note: |
you can think like this: the longer the word, the
more complex the meaning. For instance:
Electronic equipment is composed of electrical components, and
electrical components convey electric power/current. |
|
excrement, feces, stool, crap, shit, defecation, manure,
poop, etc. |
| |
| excrement |
hypernomy (hypernymy) of all below. Actually, excrement is ex
(out) + crete (make go, send) + ment (n.) So, it includes liquid
as well as solid excrement, but herein below, only solid excrement is
discussed. |
| feces |
scientist's word (always plural) |
| stool |
doctor's word (countable [C]) |
| crap |
French word (uncountable [U]) |
| shit (bad word) |
English slang (click here for more
info) [U] (WARNING: This word is NOT polite). |
| defecation |
thing defecated (thing excreted through the anus) [U] |
| manure |
farmer's word [U] |
| poop |
slang word, much more socially acceptable in speech than
other words [U] |
| poo poo |
child's word (usually for one's own solid excrement) [U] |
| doo doo |
child's word (usually for excrement not one's own) [U] |
| accept, receive, take |
| |
| accept |
to take something given mentally |
| receive |
to take something given physically |
| take |
to let something be given OR to obtain something NOT given |
| - |
Sample sentences:
- I accepted the information gladly.
- I received the reward money.
- But, I did not accept the generosity of my benefactor, and returned
the money.
- I extended my hand, and he took it.
- She took my book without permission. |
|
include, contain, have |
| |
| include |
to have (sth, which is abstract, untouchable) |
| contain |
to have (sth, which is concrete, touchable) |
| have |
to possess (sth, either abstract or concrete) [hypernym] |
| |
Sample sentences:
- English includes many words, and some words include many meanings.
- Books generally contain many words on their pages.
- English has many words and Books generally have many words. |
|
be made of, be made from, be composed of, consist
of |
| |
| be made of |
Where the component has retained much of its original
form, "be made of" is used.
Example: Glasses are made of glass. |
| be made from |
Where the component has been altered to the point where it
is no longer recognizable, "be made from" is used.
Example: Glass is made from sand. |
| be composed of |
The word "compose" includes two morphemes:
"com" + "pose". "com" means
'together' and "pose" means 'put'. When something is
"composed", two or more things are put together, usually
manually.
Example: A song is composed of words and music. |
| consist of |
The word "consist" includes two morphemes:
"con" + "sist". "con" means
'together' and "sist" means 'exist'. So,
"consist" means two or more things exist together.
Example: My family consists of two people, my son and me. |
| land, territory, earth,
ground, soil, dirt |
| |
| land |
could be considered a hypernym of all below,
but generally speaking, it is used the same as territory |
| territory |
the possessed land of some person or country |
| earth |
the planet upon which we live [sometimes used as soil] |
| ground |
the surface of the planet upon which we live |
| soil |
the portion of the earth in which plants grow |
| dirt |
the portion of the earth in which plants CAN grow, but
generally do NOT grow.
Example: I traveled on a dirt road.
|
|
beach, shore, coast, ~side, bank |
| |
| beach |
the land near a body of water, which consists of particles
of sand |
| shore |
the land near a body of water, which consists of any kind
of sand, dirt or soil |
| coast |
the length of land that connects one side of a continent
with a sea or ocean |
| ~side |
hypernomy (hypernymy) of all these synonyms |
| bank |
a vertical, near vertical, or steep land-water
connection. [usually used for a river bank, but can be used for
lakes and seas as well] |
| wide, broad, vast, huge |
| |
| wide |
(a) very long measurement, one dimensional and horizontal
Example: The valley is very wide.
(b) the shorter of two measurements of a dimensional figure or of a plot of
land (opp. long)
Example: My land is 100 meters long by 50 meters wide. |
| broad |
(a) same as wide (a)
(b) abstractly wide
Example: He has a broad mind. (He is broad-minded). |
| vast |
VERY long AND VERY wide (horizontally) [generally 2 dimensions] |
| huge |
long and wide and tall [3-dimensions] |
|
had better / have to & must / ought to &
should |
| |
| pre-note: |
it is important not to distinguish the lexical/linguistic
items above by definitions alone, but ALSO BY FUNCTION !!! |
| had better |
The function of this lexical item is WARNING.
The item "had better ((do sth))" is often collocated with
"or else...", suggesting a negative consequence of NOT doing
that thing.
For example: "You had better not stick up your
middle finger at another motorist in America, or else you might
become a victim of road rage." See Idioms
Page for definition of "road rage". |
| have to & must |
With these two linguistic items, we must look at TWO TYPES
OF FUNCTION: SEMANTIC FUNCTION and GRAMMATICAL FUNCTION.
While the Semantic Function is the same for both linguistic items,
the Grammatical Functions are different...
SEMANTIC FUNCTION: to explicate a situation where there is no
other choice, i.e., it is required, and/or compulsory.
GRAMMATICAL FUNCTIONS:
In "have + to-infinitive" we see that "have" is
functioning just as any normal verb, which is collocated with another
verb.
But "must" functions as an "auxiliary verb".
Furthermore, while some auxiliary verbs, such as "can" have
a past tense, there is no past (nor a future tense) for
"must". |
| ought to & should |
The semantic function of these two linguistic items is
VERY different from the ones above.
SEMANTIC FUNCTIONS:
1. Giving advice or suggestion
2. Explicating the moral or ethical thing to do
3. Obligation
NOW, let me explain what "obligation" means, because most
Asian bilingual lexicons are WRONG! Look at the diagram below:
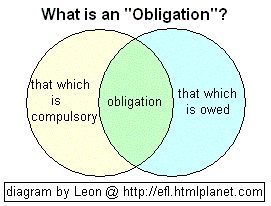
As you can see, obligation reaches into the realm of "that which
is compulsory" as well as into the realm of "that which is
owed".
The semantic function of "should" is the kind of obligation
which is "owed", NOT compulsory.
That which is compulsory belongs to the semantic function of
"have to" or "must".
Example: I should raise my son. Why? Not because I
am compelled to do so, but because I owe it to him, being his natural
father. I have a moral obligation to raise my son. |
| home, house, housing,
abode, domicile, dwelling, dormitory, barracks |
| |
| home |
Home is any place where someone lives.
It could be the street, a car, or even a city, or country. In a
way, it could be considered a hypernym of all words below |
| house |
a home made for one family [US]. [in
the UK, it would be called a "detached house", because most
houses are duplexes in the UK. See ABC Page
for differences between US and UK English.] |
| housing |
a container or covering |
| abode |
a place to abide |
| domicile |
[from French] meaning: home |
| dwelling |
a place to dwell |
| dormitory |
a place to sleep |
| barracks |
a place for military personnel to sleep |
| attire, apparel, clothes,
clothing, garment, vestibule, wear |
| |
| attire |
"attire" is an interesting word, which appears
to originate from "tir", an Old English word meaning
"glory", and further back, possibly from a Germanic word which
means "adorn". So, "attire" is anything which
adorns the human body (it would include accessories as well as
clothing). Therefore, "attire" would be a hypernym of
all words below. |
| apparel |
apparel (n.) comes from apparel (v.), which originally
meant "to get ready" (in French). So,
"apparel" [U] is the clothing that makes one appear
"ready" to go out. |
| clothes |
[plural of cloth /kla /,
"clothes" is pronounced: /klos/ ] /,
"clothes" is pronounced: /klos/ ]
Clothes [C] any attire made of cloth. |
| clothing |
same as clothes [but "clothing" is UNcountable] |
| garment |
[from French, [C] an article of clothing or amour |
| vestibule |
[from Latin] [C] place to put clothing; a closet |
| wear |
anything worn on the body |
| kinds of attire |
| |
| dress |
"dress" as a verb, means "to attire"
(put attire on), but as a noun, it only denotes a woman's gown |
| gown |
an article of clothing, which has no pants (like a long
shirt) |
| dressing gown |
[UK] a robe to cover ones sleeping clothes |
| night gown |
[US] same as dressing gown |
| vestment |
[from Latin] special clothing of someone in authority, the
clothing signifies the authority of the wearer |
| underwear |
anything worn under ones regular outerwear |
| pants |
[in UK, pants = underpants; [in US, pants = trousers] |
| trousers |
two cloth coverings for one's legs, joined at the hip,
covering the legs and loins and hips. |
| shirt |
an upper garment for ones arms and/or torso |
| blouse |
a woman's shirt |
| skirt |
a single cloth circling the legs (either partially or
entirely) and the loins and hips. |
| shoes |
attire for one's feet (usually made of leather, but
sometimes made of thick, durable cloth and rubber) |
| socks |
attire for one's feet (made of cloth) |
| pajamas |
attire for sleeping (not a kind of underwear) [Some
people sleep in their underwear ONLY... that is NOT pajamas!] |
| for more info: |
see my ATTIRE page.
(if link doesn't work, it means page is under construction, please
try back later). |
| faculty, staff |
| |
| faculty |
[U] "the teaching staff and those members of
the administrative staff having academic rank in a college, university,
or other educational institution or one of its divisions" (Merriam-Webster's
Unabridged Dictionary) |
| staff |
[U] all employees of a given company or institution or
department |
| folktale, folklore, legend,
myth |
| |
| folktale |
[C] a story which has been recounted by word of mouth from
generation to generation. It may, at last, have become written,
but was not originally written. |
| folklore |
[U] all folktales |
| legend |
a folktale, which purports to be true, in part.
Generally, the person was a real person, but the characteristics and/or
deeds attributed to that person have been exaggerated over time. |
| myth |
a folktale, which is totally UNTRUE, but was meant to
explain the universe, and nature, and creation thereof. (Probably
were children's tales in ancient times; like bedtimes stories). |
| |
English |
|

Spanish
|

Korean |

Mongolian |

Chinese |
|

Parents of
Homeschool
|
|

Halloween
|
|

Thanksgiving
|
|

Winter Solstice
|
|
Christmas
|
|

New Years
|
|

Chinese Lunar
New Year
|
|

Valentine's
|
|

|
|

Easter
|
|

All About
Dr. Seuss
|
|

Roald Dahl
|
|

Prepper's
Pen |
|

Ways to
Help
Leon's Planet
|
|